| homepage Research Research Highlights |
| Progress in Estimating Fire Counts and Radiative Power Using Satellite Optical and Microwave Vegetation Indices with Random Forest Method |
| Date: 2025-03-12 Author: SKLFS Source: SKLFS |
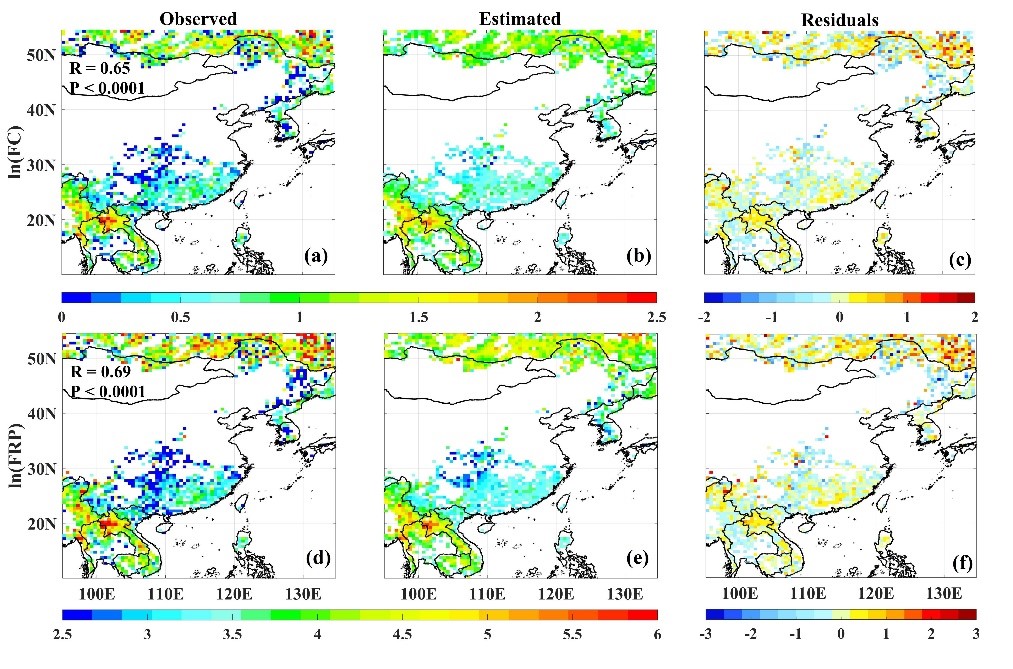
Fuel properties, such as fuel moisture content and availability, are critical determinants of fire counts (FC) and fire radiative power (FRP). This is because they directly influence fuel flammability, combustion efficiency, and radiant energy release. Satellite remote sensing is a powerful tool for monitoring fuel properties at large scales. Prof. Rui Li, from the State Key Laboratory of Fire Science and the School of Earth and Space Sciences at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), has utilized a machine learning method to gain a better understanding of continental fire properties. In this study, the random forest (RF) model was employed, with microwave - based Emissivity Difference Vegetation Index (EDVI) and optical normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) serving as key fuel properties. These indices were used to unravel the physical driving mechanisms of forest fires and to estimate daily FC and FRP over East Asia.The results indicated a good agreement between the estimated FC and FRP and satellite observations. Specifically, the spatial R was 0.59 for FC and 0.63 for FRP, while the temporal R was 0.80 for FC and 0.81 for FRP. The study found that integrating EDVI and NDVI into the RF model enhanced model performance and reduced systematic errors compared to the model without vegetation variables. This research was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres and was selected by the editorial board to be featured on AGU's social media platforms, an honor bestowed on fewer than 2% of AGU papers. The Ph.D. student Jiawei Duan was the first author of this study. Jiawei Duan, Jiheng Hu, Yuyun Fu, Qingyang Liu, Rui Li* & Yipu Wang (2025). Estimation of fire counts and fire radiative power using satellite optical and microwave vegetation indices with random forest method. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 130, e2024JD041680. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041680
Mean estimations of FC and FRP based on established RF model over East Asia, (a) and (d) are the observations of ln (FC) and ln (FRP), (b) and (e) are the estimations of ln (FC) and ln (FRP), (c), and (f) are the residuals between observations minus estimations of ln (FC) and ln (FRP). R represents the spatial correlation coefficients between observations and estimations for ln (FC) and ln (FRP).
The post of this study published at 05:00 PM (EST) on 21 Mar 2025on AGU social media https://x.com/theAGU
|
|
|
||
|
|
| Relevant link | ||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||